1999 PCED On Board Diagnostics II |
SECTION 5: Pinpoint Tests |
HE1 DTC P1400: DETERMINE PRESENT DPFEGR PID VOLTAGE
- Key on, engine off.
- Access DPFEGR PID.
Is DPFEGR PID voltage less than 0.2 volt?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Fault is currently present. KEY OFF. GO to HE2
.
|
Fault is intermittent. GO to HE5
.
|
HE2 ATTEMPT TO INDUCE OPPOSITE D.P.F. EGR SENSOR VOLTAGE
- Disconnect D.P.F. EGR sensor.
- Key on, engine off.
Is DPFEGR PID value between 4.0 and 6.0 volts?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor.
|
GO to HE3
.
|
HE3 CHECK VREF AND SIG RTN CIRCUITS FOR OPEN IN HARNESS TO D.P.F. EGR SENSOR
- Measure voltage between VREF and SIG RTN circuits at the D.P.F. EGR
sensor harness connector.
Is VREF voltage between 4.0 and 6.0 volts?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
KEY OFF. GO to HE4
.
|
GO to Pinpoint Test Step C1
.
|
HE4 CHECK DPFEGR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO GROUND AND SIG RTN IN HARNESS
Is each resistance greater than 10,000 ohms?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2
, Flash EEPROM).
|
REPAIR short circuit.
|
HE5 PERFORM WIGGLE TEST ON D.P.F. EGR SENSOR AND CIRCUIT WHILE MONITORING
DPFEGR PID FOR A SUDDEN CHANGE
- While monitoring DPFEGR PID, tap on the D.P.F. EGR sensor and wiggle
the wiring while looking for a sudden change in value as an indication of an
intermittent.
Is intermittent fault found?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPAIR as necessary.
|
Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Pinpoint Test
Step Z1
.
|
HE10 DTC P1401: DETERMINE PRESENT DPFEGR PID VOLTAGE
- Key on, engine off.
- Access DPFEGR PID with a scan tool.
Is DPFEGR PID voltage greater than 4.0 volts?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Fault is currently present. KEY OFF. GO to HE11
.
|
Fault is intermittent. GO to HE19
.
|
HE11 CHECK DPFEGR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO PWR
- Disconnect D.P.F. EGR sensor.
- Key on, engine off.
- Measure voltage between DPFEGR circuit at the D.P.F. EGR sensor harness
connector and chassis ground.
Is voltage greater than 10.5 volts?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
KEY OFF. GO to HE12
.
|
GO to HE13
.
|
HE12 CHECK DPFEGR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO PWR IN HARNESS
Is voltage greater than 10.5 volts?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPAIR short circuit.
|
REPLACE damaged PCM.
|
HE13 INDUCE OPPOSITE D.P.F. EGR SENSOR VOLTAGE
- Connect a jumper wire between DPFEGR and SIG RTN circuits at the D.P.F.
EGR sensor harness connector.
Note: If a scan tool communication concern exists, key off, remove jumper
immediately and go directly to HE18
.
- Access DPFEGR PID.
Is DPFEGR PID voltage less than 0.05 volt?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REMOVE jumper. GO to HE14
.
|
Unable to induce opposite signal. KEY OFF. GO to HE16
.
|
HE14 CHECK VREF VOLTAGE TO D.P.F. EGR SENSOR
- Measure voltage between VREF and SIG RTN circuits at the D.P.F. EGR
sensor harness connector.
Is VREF voltage between 4.0 and 6.0 volts?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
GO to HE15
.
|
GO to Pinpoint Test Step C1
.
|
HE15 CHECK DPFEGR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO VREF IN HARNESS
- Disconnect PCM.
- Measure resistance between DPFEGR and VREF circuits at the PCM harness
connector. (For LS6/LS8 measure to both VREF pins.)
Is resistance greater than 10 K ohms?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor.
|
REPAIR short circuit.
|
HE16 CHECK DPFEGR CIRCUIT FOR OPEN IN HARNESS
- Disconnect PCM.
- Measure resistance of DPFEGR circuit between PCM harness connector pin
and D.P.F. EGR sensor harness connector.
Is resistance less than 5.0 ohms?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
GO to HE17
.
|
REPAIR open circuit.
|
HE17 CHECK SIG RTN CIRCUIT FOR OPEN IN HARNESS
- Measure resistance of SIG RTN circuit between PCM harness connector pin
and D.P.F. EGR sensor harness connector.
Is resistance less than 5.0 ohms?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2
, Flash EEPROM).
|
REPAIR open circuit.
|
HE18 CHECK DPFEGR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO VREF IN HARNESS
- Disconnect PCM.
- Measure resistance between DPFEGR and VREF circuits at the PCM harness
connector. (For LS6/LS8 measure to both VREF pins.)
Is resistance greater than 10,000 ohms?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2
, Flash EEPROM).
|
REPAIR short circuit.
|
HE19 COMPLETE A WIGGLE TEST ON D.P.F. EGR SENSOR AND CIRCUIT WHILE
MONITORING DPFEGR PID FOR A SUDDEN CHANGE
- While monitoring DPFEGR PID, tap on the D.P.F. EGR sensor and wiggle
the wiring while looking for a sudden change in value as an indication of an
intermittent.
Is intermittent fault found?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPAIR as necessary.
|
Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Pinpoint Test
Step Z1
.
|
HE20 DTC P0402: CHECK FOR EGR FLOW AT IDLE WITH EGR VACUUM HOSE DISCONNECTED
Note: If DTC P1405 is in continuous memory, diagnose that first starting with
HE50.
- Disconnect vacuum hose at EGR valve and plug hose.
- Run Key On Engine Running (KOER) Self-Test.
Is KOER DTC P0402 output or unable to run KOER Self-Test due to engine
stall or no start?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
KEY OFF. INSPECT pressure hoses first for pinching and icing. If OK,
REMOVE and INSPECT the EGR valve and EGR tube for signs of contamination,
unusual wear, carbon deposits, binding and other damage. REPAIR as necessary.
|
RECONNECT vacuum hose to EGR valve. GO to HE21
.
|
HE21 CHECK FOR EGR FLOW AT IDLE WITH EGR VACUUM HOSE CONNECTED
- EGR vacuum hose connected.
- Run KOER Self-Test.
Is KOER DTC P0402 output or unable to run KOER Self-Test due to engine
stall or no start?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
There is possible EGR flow at idle. GO to HE22
.
|
Fault is intermittent. INSPECT pressure hoses for pinching and icing.
REPAIR as necessary. If OK, GO to HE30
.
|
HE22 CHECK EGR SYSTEM VACUUM HOSES FOR INTEGRITY AND CONNECTION
Note: A pinched or plugged EGR vacuum hose can trap vacuum between the EGR
vacuum regulator solenoid and EGR valve not allowing the EGR valve to close.
- Trace each vacuum hose from EGR vacuum regulator solenoid and verify
that each hose is connected correctly. (Refer to vehicle vacuum diagram label.)
- Verify that the EGR valve vacuum hose is not pinched or plugged and
routed properly.
Are vacuum hoses OK?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
RECONNECT vacuum hoses. GO to HE23
.
|
REPAIR vacuum hoses as necessary.
|
HE23 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
- Disconnect pressure hoses at D.P.F. EGR sensor.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to the downstream connection at sensor
(intake manifold side of sensor or the smaller diameter pickup tube).
- Key on, engine off.
- Access DPFEGR PID and note PID value.
- Apply 27 to 30 kPa (8 to 9 in-Hg) vacuum to the D.P.F. EGR sensor and
hold for a few seconds.
- Quickly release vacuum.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must be between 0.2 and 1.3 volt with the key on
and no vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must increase to greater than 4.0 volts with the
vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID must drop to less than 1.5 volts in less than 3 seconds
when vacuum is released.
Does the DPFEGR PID voltage indicate a fault in the D.P.F. EGR sensor?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor.
|
RECONNECT D.P.F. EGR sensor. GO to HE24
.
|
HE24 CHECK FOR EGR FLOW AT IDLE WITH EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID
CONNECTOR OFF
- Disconnect vacuum hose at EGR valve and connect hose to vacuum gauge.
- Start engine and bring to an idle.
- While monitoring vacuum gauge, disconnect the EGR vacuum regulator
solenoid harness connector.
- The EGR valve requires vacuum greater than 5.4 kPa (1.6 in-Hg) to begin
to open. If the vacuum reading remains greater than 5.4 kPa (1.6 in-Hg) after
the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid is electrically disconnected, this would
indicate a mechanical fault in the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
Does the EGR vacuum remain greater than 5.4 kPa (1.6 in-Hg) at idle
even after EGR vacuum regulator solenoid is electrically disconnected?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
This indicates a fault in the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid. KEY OFF.
GO to HE25
.
|
KEY OFF. GO to HE26
.
|
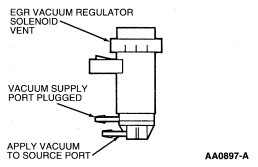
HE25 INSPECT EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID VENT FOR PLUGGING
Is the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid vent or vent filter plugged or
restricted?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPAIR EGR vacuum regulator solenoid as necessary. If unable to repair,
REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
|
REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
|
HE26 MEASURE EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID COIL RESISTANCE
- Measure resistance across EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
Is resistance between 26 and 40 ohms?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
GO to HE27
.
|
REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
|
HE27 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO GROUND IN HARNESS
Is resistance greater than 10,000 ohms?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
GO to HE28
.
|
REPAIR short circuit.
|
HE28 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO VREF
- Measure resistance between EGRVR and VREF circuits at the PCM harness
connector. (For LS6/LS8 measure to both VREF pins.)
Is resistance greater than 10,000 ohms?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2
, Flash EEPROM).
|
REPAIR short circuit.
|
HE30 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
- Disconnect pressure hoses at D.P.F. EGR sensor.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to the downstream connection at sensor
(intake manifold side of sensor or the smaller diameter pickup tube).
- Key on, engine off.
- Access DPFEGR PID and note PID value.
- Apply 27 to 30 kPa (8 to 9 in-Hg) vacuum to the D.P.F. EGR sensor and
hold for a few seconds
- Quickly release vacuum.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must be between 0.2 and 1.3 volt with the key on
and no vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must increase to greater than 4.0 volts with the
vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID must drop to less than 1.5 volts in less than 3 seconds
when vacuum is released.
Does the DPFEGR PID voltage indicate a fault in the D.P.F. EGR sensor?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor.
|
RECONNECT D.P.F. EGR sensor. GO to HE31
.
|
HE31 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR VOLTAGE WHILE EXERCISING EGR VALVE
- Key on, engine off.
- View DPFEGR PID and make note of voltage.
- Typical D.P.F. EGR sensor voltage with no EGR flow is between 0.2 and
1.3 volt.
- Disconnect vacuum hose at EGR valve and plug hose.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to EGR valve.
- Start engine and bring to idle.
- Observe DPFEGR PID at idle and compare to the key on engine off
voltage. (A higher voltage at idle could be due to a non-seating EGR valve.)
- Apply just enough vacuum to EGR valve to open it 7-10 kPa (2-3 in-Hg)
without stalling engine and release vacuum. Repeat several times while
observing DPFEGR PID. (DPFEGR PID voltage must increase as valve begins to
open and return to initial value as vacuum is released. A slow to return
voltage could be an indication of a binding or a slow-closing EGR valve.)
Does the DPFEGR PID voltage indicate an open, binding or slow-closing
EGR valve?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REMOVE and INSPECT the EGR valve for signs of contamination, unusual
wear, carbon deposits, binding and other damage. REPAIR as necessary.
|
KEY OFF. GO to HE32
.
|
HE32 MONITOR EGR VALVE VACUUM WHILE WIGGLING EGRVR CIRCUIT
Note: An intermittent short to GND in the EGRVR circuit will cause the vacuum
applied to the EGR valve to be higher than normal while the short is present.
The vacuum available at the EGR valve at idle is normally below 3.4 kPa (1.0
in-Hg) and it takes about 5.4 kPa (1.6 in-Hg) for the valve to begin to open.
- Remove hand vacuum pump.
- Connect vacuum gauge to EGR valve vacuum hose.
- Key on, engine running.
- Observe vacuum gauge for an indication of a fault while performing the
following:
- Lightly tap on the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid; wiggle the EGR vacuum
regulator solenoid connector and vehicle harness between solenoid and PCM. A
fault is indicated by a sudden jump in vacuum reading.
Is intermittent fault found?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
ISOLATE fault and REPAIR as necessary.
|
RECONNECT vacuum hose. KEY OFF. GO to HE33
.
|
HE33 INSPECT EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID AND VACUUM HOSES FOR POTENTIAL
PLUGGING
- Remove EGR vacuum regulator solenoid vent filter and inspect for
contamination and excessive water absorption. (In cold climate, excessive
water in filter could freeze and plug the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid vent.)
- Inspect EGR vacuum hose for possible blockage or pinching.
Is EGR vacuum regulator solenoid vent or filter contaminated or vacuum
hose plugged?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPAIR EGR vacuum regulator solenoid or EGR vacuum hose as necessary.
|
Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Pinpoint Test
Step Z1
.
|
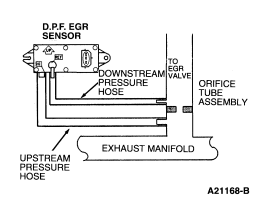
HE50 DTC P1405: INSPECT UPSTREAM PRESSURE HOSE CONNECTIONS
- Inspect upstream hose at D.P.F. EGR sensor and orifice tube assembly
for disconnect or poor connection.
Is hose off or poorly connected?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPAIR as necessary. COMPLETE EGR Monitor Repair Verification Drive
Cycle (Refer to Section 2
, Drive Cycles).
|
GO to HE51
.
|
HE51 INSPECT UPSTREAM PRESSURE HOSE FOR PLUGGING
Note: It is essential that the D.P.F. EGR pressure hose used is the correct
repair part and not a substitute.
- Visually inspect upstream pressure hose routing. Hose must not be
pinched or have dips in it where water could settle or freeze.
- Remove upstream pressure hose and carefully inspect for plugging, water
or leaks.
Is there a fault detected in the hose?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPAIR or REPLACE upstream pressure hose as necessary. COMPLETE EGR
Monitor Repair Verification Drive Cycle (Refer to Section 2
, Drive Cycles).
|
GO to HE52
.
|
HE52 CHECK ORIFICE TUBE ASSEMBLY AND D.P.F. EGR SENSOR
- Inspect the upstream connection on the D.P.F. EGR sensor for plugging
or damage at the sensor.
- Inspect the exhaust manifold side pressure pickup tube at the orifice
tube assembly for plugging or damage.
Is the D.P.F. EGR sensor or orifice tube assembly plugged or damaged?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPAIR or REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor or orifice tube assembly as
necessary. COMPLETE EGR Monitor Repair Verification Drive Cycle (Refer to
Section 2
, Drive Cycles).
|
GO to HE53
.
|
HE53 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
- Disconnect pressure hoses at D.P.F. EGR sensor.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to the downstream connection at sensor
(intake manifold side of sensor or the smaller diameter pickup tube).
- Key on, engine off.
- Access DPFEGR PID and note PID value.
- Apply 27 to 30 kPa (8 to 9 in-Hg) vacuum to the D.P.F. EGR sensor and
hold for a few seconds.
- Quickly release vacuum.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must be between 0.2 and 1.3 volt with the key on
and no vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must increase to greater than 4.0 volts with the
vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID must drop to less than 1.5 volts in less than 3 seconds
when vacuum is released.
Does the DPFEGR PID voltage indicate a fault in the D.P.F. EGR sensor?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor. COMPLETE an EGR Monitor Repair Verification
Drive Cycle (Refer to Section 2
, Drive Cycles).
|
Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Pinpoint Test
Step Z1
.
|
HE60 DTC P1406: INSPECT DOWNSTREAM PRESSURE HOSE CONNECTIONS
Note: If the fault is currently present, DTC P1408 will be output in Key On
Engine Running (KOER) Self-Test.
- Inspect downstream hose at D.P.F. EGR sensor and orifice tube assembly
for disconnect or poor connection.
Is hose OFF or poorly connected?

|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPAIR as necessary.
|
GO to HE61
.
|
HE61 INSPECT DOWNSTREAM PRESSURE HOSE FOR PLUGGING
Note: It is essential that the D.P.F. EGR sensor pressure hose is the correct
repair part and not a substitute.
- Visually inspect downstream pressure hose routing. Hose must not be
pinched or have dips in it where water can settle or freeze.
- Remove downstream pressure hose and carefully inspect for plugging,
water or leaks.
Is there a fault detected in the hose?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPAIR or REPLACE as necessary.
|
GO to HE62
.
|
HE62 CHECK ORIFICE TUBE ASSEMBLY AND D.P.F. EGR SENSOR
- Inspect the connections at the D.P.F. EGR sensor for plugging or damage.
- Inspect the intake manifold side pressure pickup tube and orifice tube
assembly for plugging, loose connection or damage.
Is the D.P.F. EGR sensor or orifice tube assembly plugged, loose or
damaged?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPAIR or REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor or orifice tube assembly as
necessary.
|
GO to HE63
.
|
HE63 CHECK EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
- Disconnect pressure hoses at D.P.F. EGR sensor.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to the downstream connection at sensor
(intake manifold side of sensor or the smaller diameter pickup tube).
- Key on, engine off.
- Access DPFEGR PID and note PID value.
- Apply 27 to 30 kPa (8 to 9 in-Hg) vacuum to the D.P.F. EGR sensor and
hold for a few seconds.
- Quickly release vacuum.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must be between 0.2 and 1.3 volt with the key on
and no vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must increase to greater than 4.0 volts with the
vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID must drop to less than 1.5 volts in less than 3 seconds
when vacuum is released.
Does the DPFEGR PID voltage indicate a fault in the D.P.F. EGR sensor?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor.
|
Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Pinpoint Test
Step Z1
.
|
HE70 DTC P0401: RUN KOER SELF-TEST
Is KOER DTC P1408 output?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
Fault is currently present. GO to HE71
.
|
GO to HE90
.
|
HE71 DTC P1408: RETRIEVE CONTINUOUS MEMORY DTCS
Note: If any DTC other than DTC P1406 is output, record DTC and refer to
Diagnostic Trouble Code Charts in Section 4
after completing this Pinpoint Test.
- Retrieve all Continuous Memory DTCs.
Is DTC P1406 output?
HE72 RUN KOER SELF-TEST WHILE MONITORING EGR VACUUM
- Disconnect vacuum hose at EGR valve and connect hose to a vacuum gauge.
Note: Since the EGR vacuum hose is disconnected, ignore DTCs during this KOER
Self-Test.
- Run Key On Engine Running (KOER) Self-Test while monitoring gauge.
Approximately 30 seconds into test, EGR flow will be requested for a few
seconds. The vacuum at this time should increase above 5.4 kPa (1.6 in-Hg) to
open the valve.
Does the vacuum increase to 10 kPa (3.0 in-Hg) or greater at any time
during KOER Self-Test?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
The vacuum indicated is sufficient to open the EGR valve. Fault is
unlikely to be in EGR vacuum control system. KEY OFF. GO to HE73
.
|
The vacuum indicated is insufficient to open the EGR valve. KEY OFF. GO
to HE80
.
|
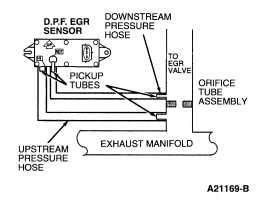
HE73 INSPECT D.P.F. EGR SENSOR PRESSURE HOSES
- Visually inspect both pressure hoses for reversed connection at D.P.F.
EGR sensor or at orifice tube assembly.
- Inspect both hoses for improper routing. Hoses should not be pinched or
have dips where water could settle or freeze.
- Inspect both hoses for leaks and blockage.
- Inspect D.P.F. EGR sensor and orifice tube assembly for blockage or
damage at the pickup tubes.
Is a fault detected?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPAIR pressure hoses as necessary.
|
GO to HE74
.
|
HE74 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
- Disconnect pressure hoses at D.P.F. EGR sensor.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to the downstream connection at sensor
(intake manifold side of sensor or the smaller diameter pickup tube.)
- Key on, engine off.
- Access DPFEGR PID and note PID value.
- Apply 27-30 kPa (8-9 in-Hg) vacuum to the D.P.F. EGR sensor and hold
for a few seconds.
- Quickly release vacuum.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must be between 0.2 and 1.3 volt with the key on
and no vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must increase to greater than 4.0 volts with the
vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID must drop to less than 1.5 volts in less than 3 seconds
when vacuum is released.
Does the DPFEGR PID voltage indicate a fault in the D.P.F. EGR sensor?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor.
|
RECONNECT pressure hoses. GO to HE76
.
|
HE76 CHECK EGR VALVE FUNCTION BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
- Disconnect vacuum hose at EGR valve and plug hose.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to EGR valve.
- Start engine and bring to idle.
- Access DPFEGR and RPM PIDs.
- Slowly apply 27 to 34 kPa (8 to 10 in-Hg) of vacuum to the EGR valve
and hold it for 10 seconds. If engine wants to stall, increase rpm with
throttle to maintain a minimum of 1000 rpm.
- Look for the following:
- EGR valve starts opening at about 5.4 kPa (1.6 in-Hg) vacuum indicated
by increasing DPFEGR PID voltage.
- DPFEGR PID voltage increasing until EGR valve is fully open. DPFEGR PID
must read 2.5 volts minimum with full vacuum applied.
- DPFEGR PID voltage steady when vacuum is held. If voltage drops within
a few seconds, the EGR valve or vacuum source can be leaking.
Does the DPFEGR PID voltage indicate that the EGR valve is operating as
described in this test?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
GO to HE85
.
|
REMOVE and INSPECT the EGR valve for signs of contamination, unusual
wear, carbon deposits, binding, leaking diaphragm and other damage. If EGR
valve is OK, look for an obstructed EGR port in the intake manifold or plugged
orifice tube assembly. REPAIR as necessary.
|
HE80 CHECK VACUUM SOURCE AND VACUUM HOSES TO AND FROM EGR VACUUM REGULATOR
SOLENOID
- Inspect vacuum lines between vacuum source and EGR vacuum regulator
solenoid and between EGR vacuum regulator solenoid and EGR valve for leaks,
kinks, disconnects, blockage, routing or any damage.
- Disconnect vacuum hoses at EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
- Connect EGR vacuum regulator solenoid vacuum source hose to a vacuum
gauge.
- With engine warm and at idle, take vacuum gauge reading.
Is the vacuum gauge reading a minimum of 51 kPa (15 in-Hg) at idle and
vacuum lines OK?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
KEY OFF. GO to HE81
.
|
ISOLATE fault and REPAIR as necessary.
|
HE81 CHECK VPWR VOLTAGE TO EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID
- Disconnect EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
- Key on, engine off.
- Measure VPWR circuit voltage at EGR vacuum regulator solenoid harness
connector.
Is EGR vacuum regulator solenoid VPWR voltage greater than 10.5 volts?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
KEY OFF. GO to HE82
.
|
REPAIR open circuit.
|
HE82 CHECK EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID RESISTANCE
- Measure EGR vacuum regulator solenoid resistance.
Is solenoid resistance between 26 and 40 ohms?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
GO to HE83
.
|
REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
|
HE83 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO PWR IN HARNESS
Is voltage greater than 1.0 volt?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPAIR short circuit.
|
KEY OFF. GO to HE84
.
|
HE84 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR OPEN IN HARNESS
- Measure resistance of EGRVR circuit between PCM harness connector pin
and EGR vacuum regulator solenoid harness connector.
Is resistance less than 5.0 ohms?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
RECONNECT PCM and EGR vacuum regulator solenoid. GO to HE85
.
|
REPAIR open in EGRVR circuit.
|
HE85 CHECK EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID VACUUM OUTPUT CAPABILITY BY
GROUNDING EGRVR CIRCUIT
- Disconnect vacuum hose at the EGR valve and connect to a vacuum gauge.
- Key on, engine running.
- With engine at idle, jumper PCM EGRVR circuit to chassis ground.
Is vacuum gauge reading 13.5 kPa (4.0 in-Hg) or greater?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2
, Flash EEPROM).
|
REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
|
HE90 INSPECT EGR SYSTEM FOR AN INTERMITTENT FAILURE
- Visually inspect the EGR system for signs of intermittent failure.
Is a fault found?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPAIR fault as necessary.
|
GO to HE91
.
|
HE91 INSPECT D.P.F. EGR SENSOR PRESSURE HOSES
- Visually inspect both pressure hoses for reversed connection at D.P.F.
EGR sensor or at orifice tube assembly.
- Inspect both hoses for improper routing. Hoses should not be pinched or
have dips where water could settle or freeze.
- Inspect both hoses for leaks and blockage.
- Inspect D.P.F. EGR sensor and orifice tube assembly for blockage or
damage at the pickup tubes.
Is a fault detected?

|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPAIR pressure hoses as necessary.
|
GO to HE92
.
|
HE92 CHECK D.P.F. EGR SENSOR OUTPUT BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
- Disconnect pressure hoses at D.P.F. EGR sensor.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to the downstream connection at sensor
(intake manifold side of sensor or the smaller diameter pickup tube.)
- Key on, engine off.
- Access DPFEGR PID and note PID value.
- Apply 27-30 kPa (8-9 in-Hg) vacuum to the D.P.F. EGR sensor and hold
for a few seconds.
- Quickly release vacuum.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must be between 0.2 and 1.3 volt with the key on
and no vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID voltage must increase to greater than 4.0 volts with the
vacuum applied.
- The DPFEGR PID must drop to less than 1.5 volts in less than 3 seconds
when vacuum is released.
Does the DPFEGR PID voltage indicate a fault in the D.P.F. EGR sensor?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPLACE D.P.F. EGR sensor.
|
RECONNECT pressure hoses. GO to HE93
.
|
HE93 CHECK EGR VALVE FUNCTION BY APPLYING VACUUM WITH HAND PUMP
- Disconnect vacuum hose at EGR valve and plug hose.
- Connect a hand vacuum pump to EGR valve.
- Start engine and bring to idle.
- Access DPFEGR and RPM PIDs.
- Slowly apply 17 to 34 kPa (5 to 10 in-Hg) of vacuum to the EGR valve
and hold it for 10 seconds. If engine wants to stall, increase rpm with
throttle to maintain a minimum of 800 rpm.
- Look for the following:
- EGR valve starts opening at about 5.4 kPa (1.6 in-Hg) vacuum indicated
by increasing DPFEGR PID voltage.
- DPFEGR PID voltage increasing until EGR valve is fully open. DPFEGR PID
should read 2.5 volts minimum with full vacuum applied.
- DPFEGR PID voltage steady when vacuum is held. If voltage drops within
a few seconds, the EGR valve or vacuum source could be leaking.
Does the DPFEGR PID voltage indicate that the EGR valve is operating as
described in this test?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
GO to HE94
.
|
REMOVE and INSPECT the EGR valve for signs of contamination, unusual
wear, carbon deposits, binding, leaking diaphragm and other damage. If EGR
valve is OK, look for an obstructed EGR port in the intake manifold. REPAIR as
necessary.
|
HE94 INSPECT EGR VACUUM SIGNAL SUPPLY FOR INTERMITTENT FAILURE
- Disconnect plugged hose at EGR valve and connect to a vacuum gauge.
- Key on, engine running.
- Connect a jumper wire between EGRVR circuit and ground to activate the
solenoid to full on. At idle, the vacuum gauge should read above 13.5 kPa (4.0
in-Hg).
- Observe vacuum gauge for an indication of a fault while performing the
following:
- Lightly tap on the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid and wiggle the EGR
vacuum regulator solenoid connector, vacuum lines and vehicle harness between
the solenoid and PCM. A fault is indicated by a sudden drop in vacuum reading.
Is a fault indicated?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
ISOLATE fault and REPAIR as necessary.
|
Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. (In cold climates,
the EGR valve may temporarily freeze shut and thaw when the engine warms up
causing the intermittent DTC.) GO to Pinpoint Test Step Z1
.
|
HE100 EGR DIAGNOSIS BY SYMPTOM: CHECK FOR EGR FLOW WITH EGR VACUUM HOSE
DISCONNECTED AND PLUGGED
Note: Perform KOER Self-Test and repair any DTCs before proceeding with this
test.
The symptom charts have indicated possible EGR flow at idle with no EGR
diagnostic trouble codes output.
Possible causes:
- EGR valve not fully seating.
- EGR vacuum regulator solenoid vent restricted.
- Damaged EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
- Disconnect vacuum hose at EGR valve and plug hose.
- Key on, engine off.
- Access DPFEGR PID and note voltage.
- Start engine and bring to idle.
- With engine at idle, look at the DPFEGR PID voltage and compare to the
engine off reading. An increase in the voltage at idle indicates that the
differential pressure feedback EGR sensor is sensing EGR flow.
Is the DPFEGR PID voltage greater at idle by a minimum of 0.15 volt
than with the engine off?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
The DPFEGR PID voltage is indicating EGR flow at idle. Since the EGR
vacuum hose is disconnected and plugged, the fault is most likely in the EGR
valve. REMOVE and INSPECT the EGR valve for signs of contamination, unusual
wear, carbon deposits, binding and other damage. REPAIR as necessary.
|
This indicates a fault in the EGR valve vacuum supply. INSPECT the EGR
vacuum regulator solenoid vent and vent filter for restrictions. REPAIR as
necessary. If OK, REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
|
HE110 DTC P1409: CHECK EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID RESISTANCE
- Disconnect EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
- Measure EGR vacuum regulator solenoid resistance.
Is solenoid resistance between 26 and 40 ohms?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
GO to HE111
.
|
REPLACE EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
|
HE111 CHECK VPWR VOLTAGE TO EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID
- Key on, engine off.
- Measure VPWR circuit voltage at EGR vacuum regulator solenoid harness
connector.
Is voltage greater than 10.5 volts?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
KEY OFF. GO to HE112
.
|
REPAIR open in VPWR circuit.
|
HE112 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR OPEN IN HARNESS
Is resistance less than 5.0 ohms?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
GO to HE113
.
|
REPAIR open in EGRVR circuit.
|
HE113 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO POWER IN HARNESS
- Key on, engine off.
- Measure voltage between EGRVR at the PCM harness connector and battery
negative post.
Is voltage less than 1.0 volt?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
KEY OFF. GO to HE114
.
|
REPAIR short circuit.
|
HE114 CHECK EGRVR CIRCUIT FOR SHORT TO GROUND IN HARNESS
- Measure resistance between EGRVR and PWR GND circuits at the PCM
harness connector.
Is each resistance greater than 10,000 ohms?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
REPLACE PCM (refer to Section 2
, Flash EEPROM).
|
REPAIR short circuit.
|
HE120 CONTINUOUS MEMORY DTC P1409: WIGGLE EGR VACUUM REGULATOR SOLENOID
WHILE MONITORING VPWR
Note: Refer to the PCM connector pin numbers in the beginning of this
pinpoint test.
Note: If DTC P1409 was output in Key On Engine Off (KOEO) or Key On Engine
Running (KOER) Self-Test, go to HE110
to diagnose
present fault.
- Disconnect PCM.
- Key on.
- Measure voltage between EGRVR and PWR GND circuits at the PCM harness
connector.
- Voltage must read greater than 10.5 volts. For an indication of a
fault, look for this voltage to drop while performing the following:
- Lightly tap on the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid.
- Wiggle the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid connector.
- Grasp the EGR vacuum regulator solenoid harness connector and wiggle
wires between solenoid and PCM.
Is a fault indicated?
|
Yes
|
No
|
|
ISOLATE fault and REPAIR as necessary.
|
Unable to duplicate or identify fault at this time. GO to Pinpoint Test
Step Z1
.
|
 HE: Introduction
HE: Introduction  HE: Introduction
HE: Introduction