Section 01-20B: Restraints, Passive—Supplemental Air Bag System | 1993 Mustang Workshop Manual |
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Diagnostic Trouble Code 22
Safing Sensor Output Circuit Shorted To Battery Voltage
Normal Operation
The diagnostic monitor measures voltage at Pins 11 (Circuit 614, GY/O)
and 12 (Circuit 623, P/W). The voltage at these pins is controlled by two
resistors inside the diagnostic monitor (along with the resistors inside the
crash sensors—refer to Normal Operation, Diagnostic Trouble
Code 24 for more information). This voltage varies with charging system voltage
(the expected voltage at Pins 11 and 12 are shown in the chart below). If the
voltage at both of these pins exceeds 5 volts, the diagnostic monitor will
flash out Diagnostic Trouble Code 22.
Possible Causes
High voltage at Pins 11 and 12 can be caused by:
- A short in the wiring harness between Circuits 614 (GY/O) or 623
(P/W) and another wire can cause high voltage on these circuits.
NOTE: The wiring harness leading to the safing sensor and clockspring carries
higher voltage circuits that may short to Circuits 614 and 623.
- A short in the clockspring between Circuit 614 and some of the
horn or speed control wiring.
- A short across the normally open contacts of the safing sensor.
NOTE: The voltage at Circuits 611 and 612 inside the safing sensor is usually
battery voltage or higher. There should be an open circuit across the contacts
of the safing sensor if the sensor is operating normally. If the sensor
contacts are closed, the voltage on Circuits 614 and 623 would be high (at
least battery voltage).
- Vehicle charging system voltage too high. If the generator
output voltage is too high (greater than 17 volts) it may cause a Diagnostic
Trouble Code 22 to occur.
CHARGING SYSTEM VOLTAGE
| Charging System Voltage |
Voltage at PIN NO. 11 |
Voltage at PIN NO. 12 |
| 9.0 |
1.9 |
1.9 |
| 9.5 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
| 10.0 |
2.1 |
2.1 |
| 10.5 |
2.2 |
2.2 |
| 11.0 |
2.3 |
2.3 |
| 11.5 |
2.4 |
2.4 |
| 12.0 |
2.5 |
2.5 |
| 12.5 |
2.6 |
2.6 |
| 13.0 |
2.7 |
2.7 |
| 13.5 |
2.7 |
2.7 |
| 14.0 |
2.9 |
2.9 |
| 14.5 |
3.0 |
3.0 |
| 15.0 |
3.1 |
3.1 |
| 15.5 |
3.2 |
3.2 |
| 16.0 |
3.3 |
3.3 |
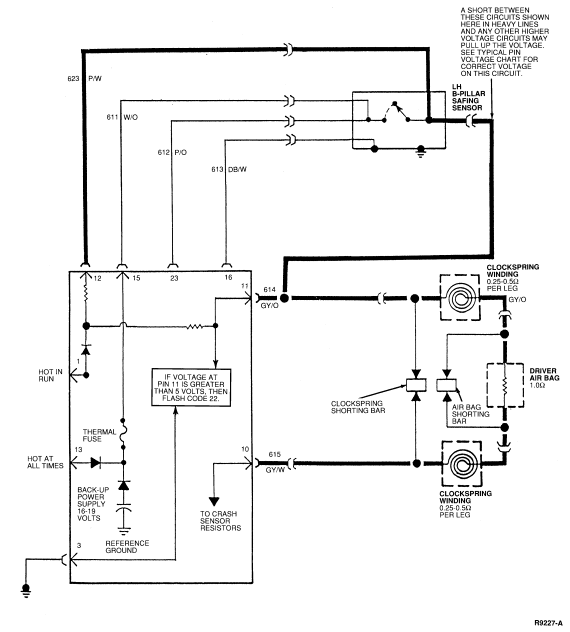
Electrical Schematic—Diagnostic Trouble Code 22
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE 22
22-1 VERIFY CONDITION
- Count diagnostic trouble code.
 Yes
Yes
GO to 22-2.
 No
No
Read the normal operation description for this diagnostic
trouble code. EXAMINE the diagnostic trouble code schematic and look for areas
where intermittent conditions would occur (connectors, splices, crimps,
etc.)
DO NOT proceed with pinpoint test until the code is flashing!
Failure to do so will result in needless replacement of the air bag system
components and repeat service.
22-2 MEASURE VOLTAGE
- Measure voltage on Circuit 614 (GY/O) Pin 11 to Pin 3 (ground).
 Yes
Yes
GO to 22-3.
 No
No
REPLACE diagnostic monitor. RECONNECT system. VERIFY system.
REACTIVATE system.
22-3 CHECK FOR WIRING SHORTS
- Disconnect diagnostic monitor.
- Disconnect LH B-pillar safing sensor.
- Measure resistance between diagnostic monitor harness connector Pin 15
(Circuit 611, W/O) and Pin 11 (Circuit 614, GY/O) and between Pins 23 (Circuit
612 P/O) and Pin 11 (Circuit 614, GY/O).
Are resistance readings infinite (open)?
 Yes
Yes
GO to 22-4.
 No
No
LOCATE and SERVICE short circuit between Circuit 611 (W/O) or
Circuit 612 (P/O) and Circuit 614 (GY/O). RECONNECT system. VERIFY system.
REACTIVATE system.
22-4 CHECK FOR SHORT CIRCUIT IN LH B-PILLAR SAFING SENSOR
- Measure resistance between LH B-pillar safing sensor connector Circuit
611 (W/O) and 614 (GY/O).
Is resistance infinite (open)?
 Yes
Yes
LOCATE and SERVICE short to B+ on Circuits 614,
615, 616, or 623.  No
No
REPLACE LH B-pillar safing sensor. RECONNECT system. VERIFY
system. REACTIVATE system.
 No
No Yes
Yes No
No
 Yes
Yes No
No Yes
Yes No
No