Section 14-02: Generator, Integral Regulator—External Fan Type | 1993 Mustang Workshop Manual |
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
On-Vehicle Tests
Tools Required:
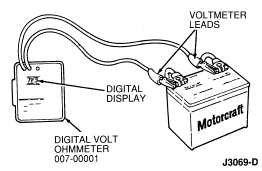
- Rotunda Digital Volt-Ohmmeter 007-00001
A volt-ohmmeter (0- to 20-volt scale) such as Rotunda Digital
Volt-Ohmmeter 007-00001 or equivalent, jumper wire and a test lamp (12-volt)
are the only tools required to perform on-vehicle tests of the complete
charging system. Test meter calibration should be checked once a year and the
date of calibration stamped on the meter face. It is recommended that this
practice be followed by all technicians to maintain test meters at acceptable
accuracy.
Troubleshooting or diagnosis is required before actual service can be
done in the electrical system. Even where an obvious condition makes
replacement of a unit necessary, find out why the unit failed. When a condition
is diagnosed correctly, unnecessary service is prevented, the time the vehicle
is out of service will be decreased, and the condition will be properly
corrected the first time.
Visual Inspection
Preliminary checks to the charging system should be made regardless of
the inoperable condition. These checks include:
- Check battery posts and cable terminals for clean and tight connections.
Clean the posts and the cables to ensure good electrical contact.
- Check for secure connections at the generator output, regulator, and engine
ground. Also check the connection at the load distribution point (starter
relay).
- Check the generator belt to ensure proper tension and no slip between the
generator pulley and the belt.
- Check the fuses/fuse links to the generator to ensure that they are not
burned or damaged. This condition, resulting in an open circuit or high
resistance, can cause erratic or intermittent charging system concerns.
Before performing charging system tests on the vehicle, note conditions
such as: slow cranking, discharged battery, top of battery wet,
generator/battery charge indicator stays on with engine running,
generator/battery charge indicator does not illuminate with ignition switch in
RUN and engine not running. This information will aid in isolating the part of
the system causing the symptom.
Isolating the Concern
Battery, starting system and lamp system concerns can be caused by poor
charging system performance. It is also reasonable to suspect the charging
system if an overload condition has occurred in another area of the electrical
system.
To avoid guesswork, it is necessary to isolate battery, charging system,
and electrical circuits to correctly identify the area where the difficulty
lies. Check the battery first before beginning any electrical system diagnosis.
The battery must be in proper state of charge and operation before the other
areas of the electrical system can perform normally.
Battery Check
Check battery to see if it has the capacity and ability to accept and
hold a charge. Refer to Section 14-01. If battery is OK, the charging system
should then be checked to see that it performs its function of keeping the
battery charged.
The battery capacity, specific gravity and cell comparison test
(non-maintenance free batteries only), will determine the ability of a battery
to accept and hold a charge. If the battery does not meet specification,
replace it with a new, fully charged battery before further diagnosis of other
areas of the electrical system.
If the battery meets required specifications, it should be fully charged
before proceeding with the diagnosis of other electrical system components.
Constant Current Drain Test
NOTE: A voltmeter is sometimes used for this test but it will react to a very
small normal drain caused by "always-on" electronic systems such as Starter
Interlock, Anti-Theft Alarm, Illuminated Entry, etc., which are so small they
cause no concern. The test lamp shows only drains which are large enough to
cause a concern.
NOTE: When the electronic instrument cluster is initially powered-up (after a
battery disconnect), the "computer" may be energized for as long as one minute
causing a 0.25A current draw before returning to the normal 0.010-0.012A
current draw. Therefore, it is important to allow at least one minute to pass
(after ammeter hookup) before observing any current measurements.
Check for current drains on the battery in excess of 50 milliamps with
all the electrical accessories off and the vehicle at rest. This test can be
performed one of three ways:
- Use a clamp-on current probe to the battery positive or negative cable.
- Use an in-line ammeter between the battery positive or negative post and
its respective cable.
- Use a 12 volt test lamp between the battery positive post and the positive
cable. If the lamp illuminates, then there is a drain somewhere in the
electrical system.
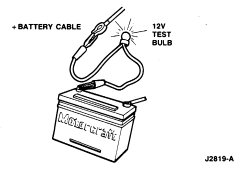
Typically, a drain of approximately one amp can be attributed to an
underhood lamp, glove compartment lamp, or rear deck lid lamp staying on
continually. Other component failures or wiring shorts may be located by
selectively pulling fuses or disconnecting fuse links to pinpoint the location
of the current drain. When the current drain is found, the current will drop
below 50 milliamps or the test lamp will go out. If the short is still not
located after checking all the fuses and fuse links, the drain may be due to
the generator/regulator. Disconnect the generator output wire from the output
stud and the regulator connector. If this eliminates the drain, check the
charging system to locate the concern.
Charging System
Tools Required:
- Rotunda Starting and Charging Tester (VAT-40) 078-00005
In order to check the charging system, the use of Rotunda Starting and
Charging Tester (VAT-40) 078-00005 or equivalent tester is suggested. Connect
the tester to the battery positive and negative posts and also connect the
current probe to the generator output lead (to measure generator output). (When
measuring generator output, the tester can also be connected to the battery
positive or negative cable. In this case, all electrical accessories must be
turned off and 10-15 amps added to the reading on the tester due to the engine
operation). With the engine running at 2000 rpm, adjust the tester load bank to
determine the output of the generator. The generator output should be near to,
or exceed the generator rating at 27°C (80°
F). Check out the charging system as indicated and service if
required.
NOTE: Refer to the Rotunda VAT-40 test procedure manual for complete directions
on checking out the charging system.
Charge Indicator System
Normal Charge Indication
The Integral Generator Regulator (IGR) has a circuit in the regulator
that will indicate a high battery voltage condition. With the IGR system, two
conditions can cause the charge indicator lamp to come on during vehicle
operation:
- No generator output: damaged generator, regulator or wiring.
- Over voltage correlation: shorted generator rotor, regulator or wiring.
If the system is working normally, the following conditions will be
present:
- With ignition switch in the OFF position, charge indicator battery symbol
is off.
- With ignition switch in the RUN position (engine not running), charge
indicator (generator) is on.
- With ignition switch in the RUN position (engine running), charge
indicator (generator) is off.
Charge Indicator Testing
- If charge indicator does not come on, disconnect wiring connector from
regulator.
- Connect a jumper wire from wiring connector 'I' terminal to battery
negative (-) post cable clamp.
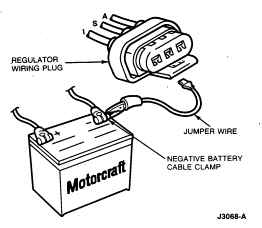
- Turn ignition switch to RUN position with engine off. If indicator does not
light, check for presence of lamp socket resistor. If resistor is present,
check for contact of lamp socket leads to the flexible printed circuit. If
good, check indicator for continuity and replace if burned out. If checks good,
perform Regulator 'I' Circuit Test.
- If indicator does light, remove jumper wire and reconnect wiring plug to
regulator. Connect voltmeter negative lead to battery negative post cable clamp
and contact voltmeter position lead to regulator 'A' terminal screw. Battery
voltage should be indicated. If battery voltage is not indicated, service 'A'
circuit wiring.
- If battery voltage is indicated, clean and tighten ground connections to
engine, generator and regulator. Tighten loose regulator mounting screws to
1.7-2.8 Nm (16-24 lb-in).
- Turn ignition to RUN position with engine off. If indicator still does not
light, replace regulator.
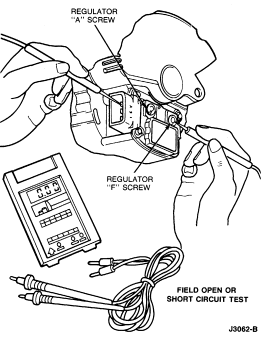
Charging System Tests
When performing charging system tests, turn off all lamps and electrical
components. Place transmission in NEUTRAL and apply parking brake.
 CAUTION: Do not make jumper wire connections except as directed. To do so may
damage regulator.
CAUTION: Do not make jumper wire connections except as directed. To do so may
damage regulator.
NOTE: Battery posts and cable clamps must be clean and tight to ensure accurate
meter indications.
Base Voltage Test
- With ignition switch in OFF position and no electrical load, connect
negative lead of voltmeter to negative battery cable clamp.
- Connect positive lead of voltmeter to positive battery cable clamp.
- Record battery voltage reading shown on voltmeter scale. This reading is
called base voltage.
No-Load Test
Tools Required:
- Rotunda Dwell-Tach-Volts Ohms Tester 059-00010
- Connect a tachometer to engine.
- Start engine and increase speed to approximately 1500 rpm. With no other
electrical load (foot off brake pedal and doors closed), voltmeter pointer
should move upward (increase) but not more than 2.5 volts above base voltage.
NOTE: The reading should be taken when voltmeter pointer stops rising. It may
take a few minutes to reach this point. If voltage increases to proper level,
perform Load Test. If the pointer continues to rise, perform the Over Voltage
Tests. If the voltage does not rise to proper level, perform Under Voltage
Tests.
Load Test
- With engine running, turn heater/air conditioner blower motor on (high
speed) and headlamps on high beam.
- Increase engine speed to approximately 2000 rpm. Voltmeter should indicate
a minimum of 0.5 volt above base voltage. If not, perform Under Voltage Tests.
If above tests indicate proper voltage readings, charging
system is operating normally. Proceed to the following tests if one or more of
the readings is different than shown above and use a test lamp to check for
battery drain.
Over Voltage Tests
If voltmeter indicates more than 2.5 volts above base voltage in No-Load
Test, follow these procedures:
- With ignition switch in RUN position (engine not running), connect
voltmeter negative lead to generator rear housing. Contact voltmeter positive
lead first to generator output connection at starter solenoid and then to
regulator 'A' screw head.
- If voltage difference between two locations is greater than 0.5 volt,
service 'A' wiring circuit to eliminate high resistance condition indicated by
excessive voltage drop.
- If over voltage condition still exists, check for loose regulator and
generator grounding screws. Tighten loose regulator grounding screws to 1.7-2.8 Nm
(16-24 lb-in).
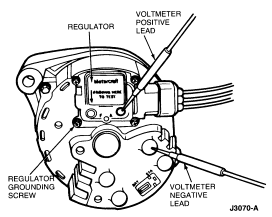
- If over voltage condition still exists, connect voltmeter negative lead to
generator rear housing. With ignition switch in OFF position, contact voltmeter
positive lead first to regulator 'A' screw head and then to regulator 'F' screw
head. Different voltage readings at two screw heads indicate a malfunctioning
regulator, grounded brush lead or a grounded rotor coil. Replace regulator,
brush holder rotor or stator, as needed.
- If same voltage reading (battery voltage) is obtained at both screw heads
in Step 4 and there is no high resistance in the ground of A+
circuit, replace regulator.
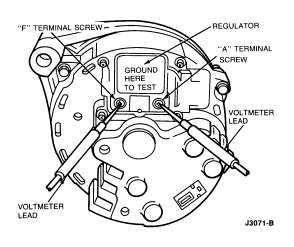
Under Voltage Tests
If voltmeter does not indicate more than 0.5 volt above base voltage,
follow these procedures:
- Disconnect wiring plug from regulator and connect an ohmmeter between
regulator 'A' and 'F' terminal screws. The meter should indicate more than 2.4
ohms. If less than 2.4 ohms is indicated, check generator for shorted rotor or
field circuit. Replace regulator, rotor or stator, as needed. Perform Load Test
after servicing.

 CAUTION: Do not replace the regulator before a shorted rotor coil or field
circuit has been serviced. Regulator damage could result.
CAUTION: Do not replace the regulator before a shorted rotor coil or field
circuit has been serviced. Regulator damage could result.
- If above ohmmeter reading is greater than 2.4 ohms, connect regulator
wiring plug and connect voltmeter negative lead to generator rear housing.
Contact voltmeter positive lead to regulator 'A' terminal screw. The meter
should indicate battery voltage. If there is no voltage, service the 'A' wiring
circuit. Perform Load Test after servicing.
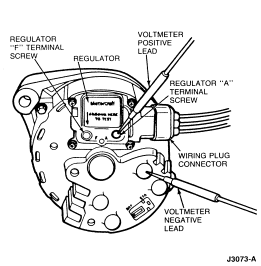
- If voltmeter indicates battery voltage, connect voltmeter ground lead to
generator rear housing. With the ignition switch in OFF position, contact
voltmeter positive lead to regulator 'F' terminal screw. The meter should
indicate battery voltage. If there is no voltage, replace generator assembly.
Perform Load Test after servicing.
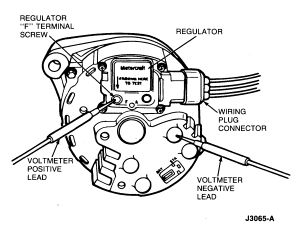
- If voltmeter indicates battery voltage, connect voltmeter negative lead to
generator rear housing. Turn ignition switch to RUN position (engine off) and
contact voltmeter positive lead to regulator 'F' terminal screw. Refer to
illustration under Step 3. The voltmeter should indicate 1.5 volts or less. If
more than 1.5 volts is indicated, perform 'I' circuit tests and service 'I'
circuit if needed. If 'I' circuit checks normal, replace regulator if needed
and perform Load Test after servicing.
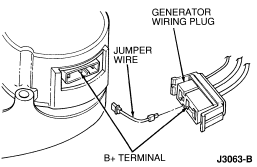
- If 1.5 volts or less is indicated, disconnect generator wiring plug and
connect a set of 12-gauge jumper wires between generator Battery Positive
Voltage (B+) terminal blades and mating wiring connector
terminals. Perform Load Test, but connect voltmeter positive to one of Battery
Positive Voltage (B+) jumper wire terminals. If voltage rises
more than 0.5 volt above base voltage, service generator-to-starter relay
wiring. Repeat Load Test, measuring voltage at battery cable clamps after
servicing.
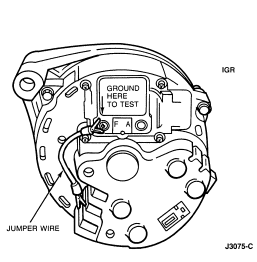
- If voltage does not rise more than 0.5 volt above base voltage, connect a
jumper wire from generator rear housing to regulator 'F' terminal. Repeat Load
Test with voltmeter positive lead connected to one of Battery Positive Voltage
(B+) jumper wire terminals. If voltage rises more than 0.5 volt,
replace regulator.
- If voltage does not rise more than 0.5 volt, service generator.
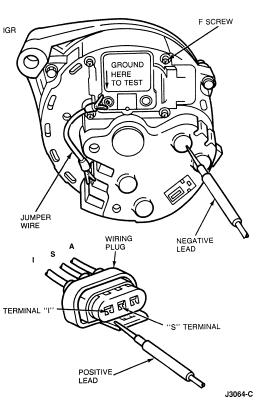
Regulator 'S' and/or 'I' Circuit Test
- Disconnect the wiring plug from the regulator. Connect a jumper wire from
the regulator 'A' terminal to the wiring plug 'A' lead. Add a jumper wire from
the regulator 'F' screw to the generator rear housing.
- With the engine idling and the voltmeter negative lead connected to battery
ground terminal, connect the voltmeter positive lead to the 'S' terminal and
then to the 'I' terminal of the regulator wiring plug. The voltage at the 'S'
circuit should read approximately one-half that of the 'I' circuit. If voltage
readings are normal, remove the jumper wire. Replace the regulator and connect
the wiring plug to the regulator. Repeat the Load Test after servicing.
- If no voltage is present, remove the jumper wire and service the damaged or
worn wiring circuit or replace generator assembly.
- Connect the voltmeter positive lead to the positive battery terminal.
Connect the wiring plug to the regulator. Repeat the Load Test.
Fuse Link Continuity
- Ensure first that battery is OK, then turn on headlamps or any accessory.
If headlamps or an accessory do not operate, fuse link is probably burned out.
- On some vehicles there are several fuse links. Use same procedure as in
Step 1 to test fuse link that protects vehicle equipment.
- To test fuse link that protects generator, ensure that battery is OK, then
check with a voltmeter for voltage at Battery Positive Voltage (B+) terminal of
generator and 'A' terminal of regulator. No voltage indicates that fuse link is
probably burned out.
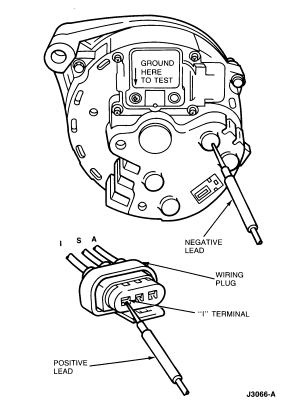
Field Circuit Drain
Connect the voltmeter negative lead to the generator rear housing for all
of the following voltage readings:
- With ignition switch turned to OFF position, contact voltmeter positive
lead to regulator 'F' terminal screw. The meter should indicate battery voltage
if system is operating normally. If less than battery voltage is indicated,
proceed with Step 2 to find cause of current drain.

- Disconnect wiring plug from regulator and contact voltmeter positive lead
to wiring plug 'I' terminal. No voltage should be indicated. If voltage is
indicated, service 'I' lead from ignition switch to identify and eliminate
voltage source.
- If no voltage was indicated in Step 2, contact voltmeter positive lead to
wiring plug 'S' terminal. No voltage should be indicated. If no voltage is
indicated, replace the regulator.
- If voltage was indicated in Step 3, disconnect wiring plug from the
generator rectifier connector. Again, contact voltmeter positive
(+) lead to regulator wiring plug 'S' terminal. If voltage is
indicated, service 'S' lead to generator plug to eliminate voltage source. If
no voltage is indicated, replace generator rectifier assembly.
Charging System Check
 WARNING: SPECIAL CARE SHOULD BE TAKEN WHEN USING THE OHMMETER NEAR "HOT"
CIRCUITS. DISCONNECT THE COMPONENT TO BE CHECKED OR THE BATTERY CABLES TO
PREVENT DAMAGE TO THE OHMMETER.
WARNING: SPECIAL CARE SHOULD BE TAKEN WHEN USING THE OHMMETER NEAR "HOT"
CIRCUITS. DISCONNECT THE COMPONENT TO BE CHECKED OR THE BATTERY CABLES TO
PREVENT DAMAGE TO THE OHMMETER.
The charging system test should be performed before testing any
individual charging system components. The component tests will determine the
type of component service required.
Test instruments used in the charging system test are a voltmeter (0-20-
or 0-30-volt scale) and an ohmmeter.
Continue through Diagnosis charts until service is completed. Then, test
system again to see if service has corrected the condition.
PINPOINT TEST A: CHARGING SYSTEM TEST—IAR GENERATOR
A1 PRELIMINARY CHECKS
- Battery terminals and cable clamps
- Wiring and ground connections to generator regulator and engine
 Yes
Yes
GO to A2.
 No
No
SERVICE and/or REPLACE as necessary. GO to A2.
A2 BASE VOLTAGE AND NO LOAD TEST
- Connect voltmeter to battery posts. Read battery voltage — this is base reading.
- Start engine, run at 1500 rpm with no electrical load.
Does voltage increase more than 2 volts?
 No
No
GO to A3.
 No increase
No increase
GO to A5.
 Yes
Yes
GO to A12.
A3 LOAD TEST
- Increase engine speed to 2000 rpm.
- Turn heater A/C, blower and headlamps on high.
Is voltage a minimum of 0.5 volt over base voltage?
 Yes
Yes
GO to A4.
 No
No
GO to A5.
A4 BATTERY DRAIN TEST — KEY OFF
- Concern can still be battery drain. Turn off ignition, install test lamp in series with positive battery cable and check to isolate symptom circuit.
Is there a battery drain?
 Yes
Yes
CHECK vehicle circuits for drain.  No
No
REFER to Section 14-01.
A5 UNDER-VOLTAGE TEST
- Check resistance between regulator 'A' and 'F' terminals on regulator.
Is resistance more than 2.4 ohms?
 No
No
CHECK generator for shorted field circuit and REPLACE if required. REPLACE regulator,if required. GO to A2.
 Yes
Yes
GO to A6.
A6 'A' TERMINAL VOLTAGE CHECK
- Measure 'A' terminal voltage.
Is there battery voltage?
 No
No
SERVICE 'A' circuit wiring.  Yes
Yes
GO to A7.
A7 'F' TERMINAL VOLTAGE CHECK — IGNITION OFF
- Measure regulator 'F' terminal voltage with ignition off.
Is there battery voltage?
 No
No
SERVICE IAR for open or grounded field circuit. GO to A2.
 Yes
Yes
GO to A8.
A8 'F' TERMINAL VOLTAGE CHECK — IGNITION ON
- Turn ignition to RUN position (engine not running).
- Measure regulator 'F' terminal voltage.
Is voltage more than 1.5 volts?
 Yes
Yes
GO to A9.
 No
No
GO to A10.
A9 'I' CIRCUIT TESTS
- Perform 'I' circuit tests.
 Yes
Yes
REPLACE regulator. GO to A2.
 No
No
SERVICE 'I' circuit wiring. GO to A2.
A10 JUMPERED LOAD TEST
- Disconnect generator plug.
- Connect jumper wires between Battery Positive Voltage (B+) blades and wiring plug.
- Repeat load test measuring voltage to generator Battery Positive Voltage (B+) output terminal from battery negative clamp.
Does voltage rise 0.5 volt or more?
 Yes
Yes
SERVICE generator to starter relay wiring. GO to A2.
 No
No
GO to A11.
A11 LOAD TEST REPEAT — 'F' TERMINAL
- Keep Battery Positive Voltage (B+) jumper wires in place.
- Connect a jumper wire from generator rear housing to regulator 'F' terminal.
- Repeat load test measuring voltage at Battery Positive Voltage (B+) output terminal.
Does voltage rise 0.5 volt or more?
 Yes
Yes
REPLACE regulator. GO to A2.
 No
No
SERVICE generator. GO to A2.
A12 OVER VOLTAGE TEST
- Turn ignition to RUN position (engine not running).
- Measure voltage at regulator 'A' terminal and starter solenoid.
Is voltage difference 0.5 volt or less?
 Yes
Yes
GO to A13.
 No
No
SERVICE 'A' circuit wiring. GO to A2.
A13 REGULATOR GROUND CHECK
- Check for loose regulator ground screws.
 Yes
Yes
GO to A14.
 No
No
SERVICE ground screws. GO to A2.
A14 ENGINE GROUND CHECK
 Yes
Yes
GO to A15.
 No
No
SERVICE engine ground. GO to A2.
A15 GENERATOR GROUND CHECK
 Yes
Yes
GO to A16.
 No
No
SERVICE generator ground. GO to A2.
A16 REPEAT NO LOAD TEST
- Start engine, run at 1500 rpm with no electrical load.
Does voltage increase more than 2 volts?
 No
No
GO to A3.
 Yes
Yes
GO to A17.
A17 'A' AND 'F' VOLTAGE CHECKS
- Measure voltage at regulator 'A' and 'F' terminals.
Are both terminal voltages battery voltage?
 Yes
Yes
REPLACE regulator. GO to A2.
 No
No
REPLACE generator assembly. GO to A2.



 CAUTION: Do not make jumper wire connections except as directed. To do so may
damage regulator.
CAUTION: Do not make jumper wire connections except as directed. To do so may
damage regulator. 








 Yes
Yes