1999 PCED On Board Diagnostics II |
SECTION 1: Description and Operation |
The Secondary Air Injection (AIR) system controls emissions during the first 20 to 120 seconds of engine operation by forcing air downstream into the exhaust manifolds to oxidize the hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide created by running rich at start up.
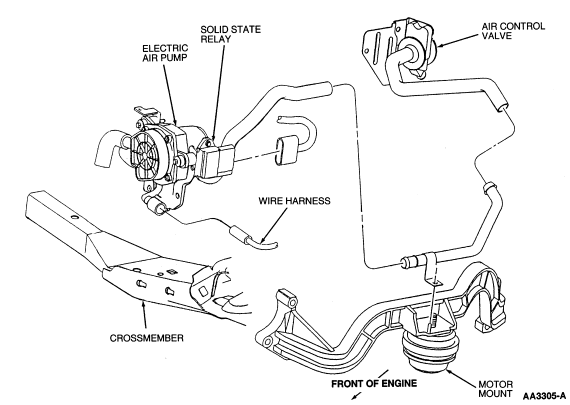
The Electric Secondary Air Injection (AIR) system consists of an electric AIR pump, single or dual combination check air injection diverter (AIR diverter) valve(s), an AIR bypass solenoid, a solid state relay, powertrain control module (PCM) and connecting wires and vacuum hoses (Figure 129) .

The electric AIR pump (Figure 130) provides pressurized air to the Secondary Air Injection system. The electric AIR pump functions independently of rpm and is controlled by the PCM. The electric AIR pump is only used for short periods of time. Delivery of air is dependent on the amount of system backpressure and system voltage. The inlet system of the AIR pump incorporates a non-serviceable filter and splash cap which helps to guard against dirt and water.

The secondary air injection bypass (AIR bypass) solenoid (Figure 131) is used by the PCM to control vacuum to the secondary air injection diverter (AIR diverter) valve. The AIR bypass solenoid is a normally closed solenoid. The AIR bypass solenoid also has a filtered vent feature to permit vacuum release.

The secondary air injection diverter (AIR diverter) valve (Figure 132) is used with the electric AIR pump to provide on/off control of air to the exhaust manifold and catalytic converter. When the electric AIR pump is on and vacuum is supplied to the AIR diverter valve, air passes the integral check valve disk. When the electric AIR pump is off, and vacuum is removed from the AIR diverter valve, the integral check valve disk is held on the seat and stops air from being drawn into the exhaust system and prevents the back flow of the exhaust into the Secondary Air Injection System.

The solid state relay (Figure 133) switches the high current required for operation of the electric AIR pump. Input control to the solid state relay comes from the powertrain control module (PCM).

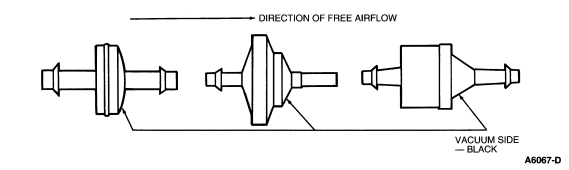
A vacuum check valve (Figure 134) blocks air flow in one direction. It allows free air flow in the other direction. The check side of this valve will hold the highest vacuum registered on the vacuum side.