1999 PCED On Board Diagnostics II |
SECTION 1: Description and Operation |
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Running Loss System Monitor
The Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Running Loss System Monitor is an
on-board strategy designed to detect a leak from a hole (opening) equal to or
greater than 1.016 mm (0.040 inch) in the EVAP Running Loss system. The proper
function of the individual components of the EVAP Running Loss system as well
as its ability to flow fuel vapor to the engine is also examined. The EVAP
Running Loss System Monitor relies on the individual components of the EVAP
Running Loss system to apply vacuum to the fuel tank and then seal the entire
EVAP Running Loss system from atmosphere. The fuel tank pressure is then
monitored to determine the total vacuum lost (bleed-up) for a calibrated
period of time. Inputs from the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor,
intake air temperature (IAT) sensor, mass air flow (MAF) sensor, vehicle speed
sensor (VSS), fuel level input (FLI) and fuel tank pressure (FTP) sensor are
required to enable the EVAP Running Loss System Monitor.
Note: During the EVAP Running Loss System Monitor Repair Verification Drive
Cycle a PCM reset will bypass the minimum soak time required to complete the
monitor. The EVAP Running Loss System Monitor will not run if the key is
turned off after a PCM reset. The EVAP Running Loss System Monitor will not
run if a MAF sensor failure is indicated. The EVAP Running Loss System Monitor
will not initiate until the Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) Monitor has completed.
The EVAP Running Loss System Monitor is executed by the individual
components of the EVAP Running Loss system as follows:
-
The function of the EVAP canister purge valve is to create a vacuum on
the fuel tank. A minimum duty cycle on the EVAP canister purge valve (75%)
must be met before the EVAP Running Loss System Monitor can begin.
-
The canister vent (CV) solenoid will close (100% duty cycle) with the
EVAP canister purge valve at its minimum duty cycle to seal the EVAP Running
Loss system from atmosphere and obtain a target vacuum on the fuel tank.
-
The fuel tank pressure (FTP) sensor will be used by the EVAP Running
Loss System Monitor to determine if the target vacuum on the fuel tank is
being reached to perform the leak check. Some vehicle applications with the
EVAP Running Loss System Monitor use a remote in-line FTP sensor. Once the
target vacuum on the fuel tank is achieved, the change in fuel tank vacuum for
a calibrated period of time will determine if a leak exists.
-
If the initial target vacuum cannot be reached, DTC P0455 (gross leak
detected) will be set. The EVAP Running Loss System Monitor will abort and not
continue with the leak check portion of the test.
If the initial target vacuum is exceeded, a system flow fault exists
and DTC P1450 (unable to bleed-up fuel tank vacuum) is set. The EVAP Running
Loss System Monitor will abort and not continue with the leak check portion of
the test.
If the target vacuum is obtained on the fuel tank, the change in the
fuel tank vacuum (bleed-up) will be calculated for a calibrated period of
time. The calculated change in fuel tank vacuum will be compared to a
calibrated threshold for a leak from a hole (opening) of 1.016 mm (0.040 inch)
in the EVAP Running Loss system. If the calculated bleed-up is less than the
calibrated threshold, the EVAP Running Loss system passes. If the calibrated
bleed-up exceeds the calibrated threshold, the test will abort and rerun the
test up to three times.
If the bleed-up threshold is still being exceeded after three tests, a
vapor generation check must be performed before DTC P0442 (small leak
detected) will be set. This is accomplished by returning the EVAP Running Loss
system to atmospheric pressure by closing the EVAP canister purge valve and
opening the CV solenoid. Once the FTP sensor observes the fuel tank is at
atmospheric pressure, the CV solenoid closes and seals the EVAP Running Loss
system.
The fuel tank pressure build-up for a calibrated period of time will be
compared to a calibrated threshold for pressure build-up due to vapor
generation.
If the fuel tank pressure build-up exceeds the threshold, the leak test
results are invalid due to vapor generation. The EVAP Running Loss System
Monitor will pass and complete.
If the fuel tank pressure build-up does not exceed the threshold, the
leak test results are valid and DTC P0442 will be set.
-
The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) is activated for DTCs P0442, P0455
and P1450 (or P446) after two occurrences of the same fault. The MIL can also
be activated for any EVAP Running Loss system component DTCs in the same
manner. The EVAP Running Loss system component DTCs P0443, P0452, P0453 and
P1451 are tested as part of the Comprehensive Component Monitor (CCM).
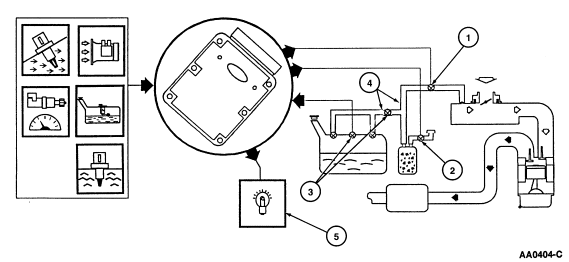
Figure 9: Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Running Loss System Monitor
