1999 PCED On Board Diagnostics II |
SECTION 1: Description and Operation |
Fuel Systems
Overview
The fuel system supplies the fuel injectors with clean fuel at
controlled pressure. The system is called Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection
(SFI). The powertrain control module (PCM) controls the fuel pump and monitors
the fuel pump circuit. The PCM also controls the duration of the on/off cycle
providing correct timing of the fuel injectors. If the injectors have been
replaced, it is necessary to clear learned values contained in the Keep Alive
Random Access Memory (RAM) in the PCM. This can be done by disconnecting the
battery or the PCM for five minutes. (Refer to Section 2
, Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) Reset, for more information.)
Three types of fuel systems used are:
- Returnable Fuel
- Mechanical Returnless Fuel
- Electronic Returnless Fuel
Returnable Fuel System
The fuel system consists of a fuel tank with a reservoir, fuel pump
module, fuel supply lines, fuel filter(s), Schrader/pressure test point, fuel
rail, fuel injectors, and fuel pressure regulator. Operation of the system is
as follows (refer to Figure 56 for all others):
-
The fuel delivery system uses the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor to
signal the PCM that the engine is either cranking or running.
-
The fuel pump logic is defined in the Fuel System control strategy and
is executed in the PCM. The PCM will ground the fuel pump relay for one second
during key on and engine off. During crank the fuel pump relay is grounded as
long as the PCM receives a CKP signal.
-
The fuel pump relay has a primary and a secondary circuit. The primary
side is controlled by the PCM and the secondary side provides B+ to the fuel
pump circuit when the relay is energized.
-
The inertia fuel shut-off (IFS) switch is used to de-energize the fuel
delivery secondary circuit in the event of a collision. The IFS Switch is a
safety device that should only be reset after a thorough inspection of the
vehicle (following a collision).
-
The fuel injector is a solenoid-operated valve that meters fuel flow to
each combustion cylinder. The fuel injector is opened and closed a constant
number of times per crankshaft revolution. The amount of fuel is controlled by
length of time the fuel injector is held open. The injector is normally closed
and is operated by 12 volt VPWR from the power relay. The ground signal is
controlled by the PCM.
-
A pressure test point valve (Schrader valve) is located on the fuel
rail. This is used to measure fuel injector supply pressure for service and
diagnostic procedures.
-
The fuel pressure regulator is attached to the fuel rail downstream of
the fuel injectors. It regulates fuel pressure supplied to the fuel injectors.
The fuel pressure regulator is a diaphragm-operated relief valve. One side of
the diaphragm senses fuel pressure and the other side is connected to the
intake manifold vacuum. Fuel pressure is established by a spring preload
applied to the diaphragm. Balancing one side of the diaphragm with manifold
vacuum maintains a constant fuel pressure drop across the fuel injectors. Fuel
pressure is high when engine vacuum is low. Excess fuel is bypassed through
the fuel pressure regulator and returned through the fuel return line to the
fuel tank.
-
There are four filtering or screening devices in the fuel delivery
system. The fuel intake sock or screen is a fine, nylon mesh mounted on the
intake side of the fuel pump. There is a fuel filter screen located at the
fuel rail side of the fuel injector. A fuel filter/screen is located in the
inlet side of the fuel pressure regulator. The fuel filter assembly is located
between the fuel pump and the pressure test point/schrader valve.
-
The fuel pump (FP) module is a device that contains both fuel pump and
fuel sender assembly. The fuel pump is located inside the reservoir and
supplies fuel through the fuel pump module manifold to the engine and the fuel
pump module jet pump.
Note: Some vehicles have the relay located in the Power Distribution Box.
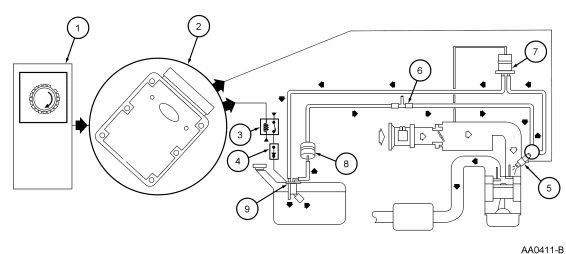
Figure 57: Fuel System - All others
Mechanical Returnless Fuel System
The fuel system consists of a fuel tank with reservoir, fuel pump, fuel
pressure regulator, fuel filter, fuel supply line, fuel rail, fuel rail pulse
damper, fuel injectors, and Schrader/pressure test point. Operation of the
system is as follows (Figure 57):
-
The fuel delivery system is enabled during crank or running mode once
the PCM receives a crankshaft position (CKP) sensor signal.
-
The fuel pump logic is defined in the fuel system control strategy and
is executed by the PCM.
-
The PCM grounds the fuel pump relay, which provides VPWR to the fuel
pump.
-
The inertia fuel shut-off (IFS) switch is used to de-energize the fuel
delivery secondary circuit in the event of collision. The IFS switch is a
safety device that should only be reset after a thorough inspection of the
vehicle (following a collision).
-
A pressure test point valve (Schrader valve) is located on the fuel
rail. This is used to measure fuel injector supply pressure for diagnostic
procedures and repairs.
-
Located on the fuel rail is a pulse damper. The pulse damper reduces
fuel system noise caused by the pulsing of the fuel injectors. The vacuum port
located on the damper is connected to manifold vacuum to avoid fuel spillage
in the event the pulse damper diaphragm were to rupture (the pulse damper
should not be confused with a fuel pressure regulator).
-
The fuel injector is a solenoid-operated valve that meters the fuel
flow to each combustion cylinder. The fuel injector is opened and closed a
constant number of times per crankshaft revolution. The amount of fuel is
controlled by the length of time the fuel injector is held open. The injector
is normally closed and is operated by 12 volt VPWR from the power relay. The
ground signal is controlled by the PCM.
-
There are three filtering or screening devices in the fuel delivery
system. The intake sock is a fine, nylon mesh screen mounted on the intake
side of the fuel pump. There is a fuel filter screen located at the fuel rail
side of the fuel injector. The fuel filter assembly is located between the
fuel pump and the pressure test point/Schrader valve.
-
The fuel pump (FP) module contains the fuel pump, fuel pressure
regulator and the fuel sender assembly. The fuel pressure regulator is
attached to the fuel pump in the fuel pump module located in the fuel tank. It
regulates fuel pressure supplied to the fuel injectors. The fuel pressure
regulator is a diaphragm-operated relief valve. Fuel pressure is established
by a spring preload applied to the diaphragm. Excess fuel is bypassed through
the regulator and returned to the fuel tank.
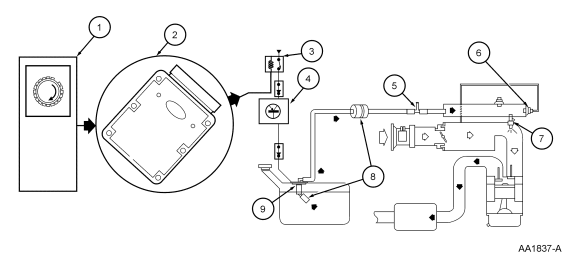
Figure 58: Fuel System—Mechanical Returnless
Electronic Returnless Fuel System
The fuel system consists of a fuel tank with reservoir, fuel pump, fuel
rail pressure sensor, fuel filter, fuel supply line, engine fuel temperature
sensor, fuel rail, fuel injectors, and Schrader/pressure test point. Operation
of the system is as follows (Figure 58) and (Figure 59):
-
The fuel delivery system is enabled during crank or running mode once
the PCM receives a crankshaft position (CKP) sensor signal.
-
The fuel pump logic is defined in the fuel system control strategy and
is executed by the PCM.
-
The PCM commands a duty cycle to the fuel pump driver module (FPDM).
-
The fuel pump driver module modulates the voltage to the fuel pump (FP)
to achieve the proper fuel pressure. Voltage for the fuel pump is supplied by
the power relay or FPDM power supply relay.
-
The fuel rail pressure (FRP) sensor provides the PCM with the current
fuel rail pressure. The PCM uses this information to vary the duty cycle
output to the FPDM to compensate for varying loads.
-
The engine fuel temperature (EFT) sensor measures current fuel
temperatures in the fuel rail. This information is used to vary the fuel
pressure and avoid fuel system vaporization.
-
The fuel injector is a solenoid-operated valve that meters the fuel
flow to each combustion cylinder. The fuel injector is opened and closed a
constant number of times per crankshaft revolution. The amount of fuel is
controlled by the length of time the fuel injector is held open. The injector
is normally closed and is operated by 12 volt VPWR from the power relay. The
ground signal is controlled by the PCM.
-
A pressure test point valve (Schrader valve) is located on the fuel
rail. This is used to measure fuel injector supply pressure for diagnostic
procedures and repairs.
-
There are three filtering or screening devices in the fuel delivery
system. The intake sock is a fine, nylon mesh screen mounted on the intake
side of the fuel pump. There is a fuel filter screen located at the fuel rail
side of the fuel injector. The fuel filter assembly is located between the
fuel pump and the pressure test point/Schrader valve.
-
The fuel pump (FP) module is a device that contains the fuel pump and
the fuel sender assembly. The fuel pump is located inside the reservoir and
supplies fuel through the fuel pump module manifold to the engine and the fuel
pump module jet pump.
-
The inertia fuel shut-off (IFS) switch is used to de-energize the fuel
delivery secondary circuit in the event of a collision. The IFS switch is a
safety device that should only be reset after a thorough inspection of the
vehicle (following a collision).
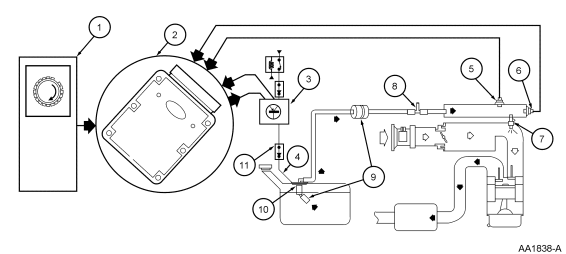
Figure 59: Fuel System—Electronic Returnless
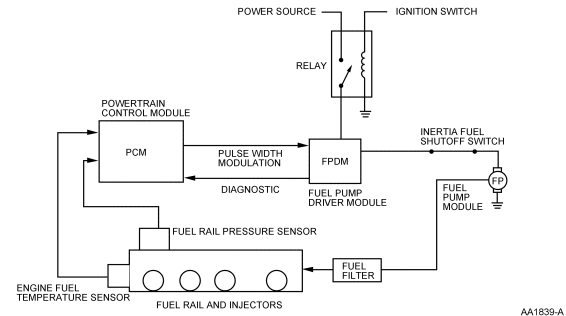
Figure 60: Typical Electronic Returnless Fuel System Schematic (NOTE: See EVTM
for proper power source and relay usage.)
Fuel Pump and Reservoir
The fuel pump module (Figure 60) is mounted inside the fuel tank
in a reservoir. The pump has a discharge check valve that maintains system
pressure after the key has been turned off to minimize starting concerns. The
reservoir prevents fuel flow interruptions during extreme vehicle maneuvers
with low tank fill levels.
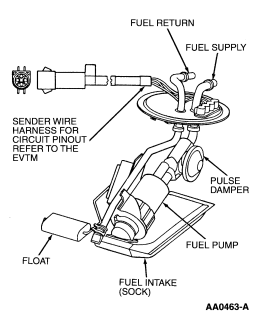
Figure 61: Fuel Pump Module
Fuel Pump Module
The fuel pump (FP) module (Figure 61) is a device that contains
the fuel pump and sender assembly. The fuel pump is located inside the FP
module reservoir and supplies fuel through the FP module manifold to the
engine and FP module jet pump. The jet pump continuously refills the reservoir
with fuel, and a check valve located in the manifold outlet maintains system
pressure when the fuel pump is not energized. A flapper valve located in the
bottom of the reservoir allows fuel to enter the reservoir and prime the fuel
pump during the initial fill.
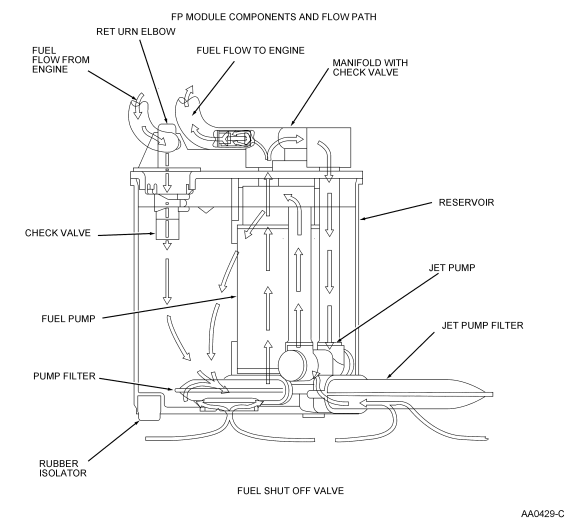
Figure 62: Fuel Pump Module (For Returnable Fuel Systems)
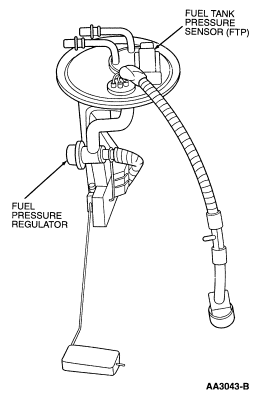
Figure 63: Mechanical Returnless Fuel Pump Module (FPM)
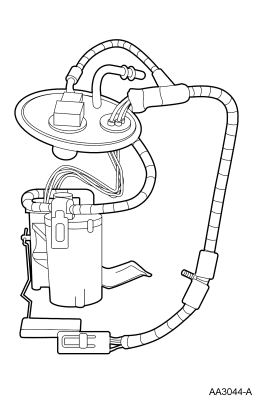
Figure 64: Electrical Returnless Fuel Pump Module (FPM)
Fuel Filters
The system contains four filtering or screening devices. Refer to the
individual component pictorial for location.
-
The fuel intake sock or screen is a fine nylon mesh sock mounted on the
intake side of the fuel pump. It is part of the assembly and cannot be
serviced separately.
-
The filter/screen at the fuel rail port of the Injectors is part of the
fuel injector assembly and cannot be serviced separately.
-
The filter/screen at fuel inlet side of the fuel pressure regulator is
part of the regulator assembly and cannot be serviced separately.
-
The fuel filter assembly is located between the fuel pump (tank) and
the pressure test point (Schrader valve) or Injectors. This filter may be
serviced.
Pressure Test Point
There is a pressure test point with a schrader fitting in the fuel rail
that relieves fuel pressure and measures the fuel injector supply pressure for
service and diagnostic procedures. Before servicing or testing the fuel
system, read any CAUTION, WARNING, and HANDLING information.
Fuel Injector
The fuel injector (Figure 64) is a solenoid-operated valve that
meters fuel flow to the engine. The fuel injector is opened and closed a
constant number of times per crankshaft revolution. The amount of fuel is
controlled by the length of time the fuel injector is held open.
The fuel injector is normally closed and is operated by 12 volt VPWR
from the electronic engine control power relay. The ground signal is
controlled by the PCM.
 CAUTION: Do not apply battery positive voltage (B+) directly to the fuel
injector electrical connector terminals. The solenoids may be damaged
internally in a matter of seconds.
CAUTION: Do not apply battery positive voltage (B+) directly to the fuel
injector electrical connector terminals. The solenoids may be damaged
internally in a matter of seconds.
The injector is the deposit resistant (DRI) type and does not have to
be cleaned. However, it can be flow checked and, if found outside of
specification, the fuel injector should be replaced.
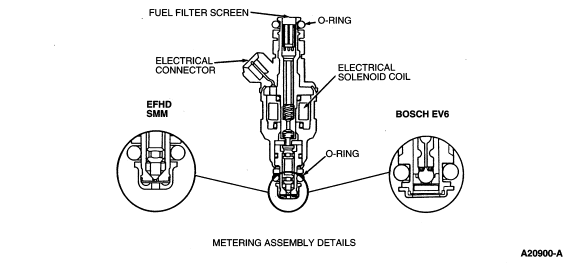
Figure 65: Fuel Injectors
Fuel Pressure Regulator
The fuel pressure regulator (Figure 65) is attached to the fuel
rail downstream of the fuel injectors. It regulates fuel pressure supplied to
the fuel injectors. The regulator is a diaphragm-operated relief valve. One
side of the diaphragm senses fuel pressure and the other side is connected to
the intake manifold vacuum. Fuel pressure is established by a spring preload
applied to the diaphragm. Balancing one side of the diaphragm with manifold
vacuum maintains a constant fuel pressure drop across the fuel injectors. Fuel
pressure is high when engine vacuum is low. Excess fuel is bypassed through
the fuel pressure regulator and returned through the fuel return line to the
fuel tank.
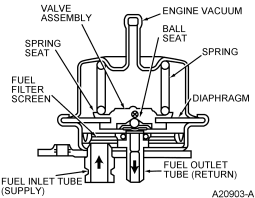
Figure 66: Fuel Pressure Regulator









 CAUTION: Do not apply battery positive voltage (B+) directly to the fuel
injector electrical connector terminals. The solenoids may be damaged
internally in a matter of seconds.
CAUTION: Do not apply battery positive voltage (B+) directly to the fuel
injector electrical connector terminals. The solenoids may be damaged
internally in a matter of seconds.
