1999 PCED On Board Diagnostics II |
SECTION 1: Description and Operation |
Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) Monitor
The HO2S Monitor is an on-board strategy designed to monitor the HO2S
sensors for a malfunction or deterioration which can affect emissions. The
fuel control or upstream HO2S is checked for proper output voltage and
response rate (the time it takes to switch from lean to rich and vice versa).
Downstream HO2S used for Catalyst Monitor are also monitored for proper output
voltage. The following illustration shows that input is required from the ECT,
IAT, MAF and CKP sensors to activate the HO2S Monitor. The Fuel System Monitor
and Misfire Detection Monitor must also have completed successfully before the
HO2S Monitor is enabled.
-
The HO2S sensor senses the oxygen content in the exhaust flow and
outputs a voltage between zero and 1.0 volt. Lean of stoichiometric (air/fuel
ratio of approximately 14.7:1), the HO2S will generate a voltage between zero
and 0.45 volt. Rich of stoichiometric, the HO2S will generate a voltage
between 0.45 and 1.0 volt. The HO2S Monitor evaluates both the upstream (fuel
control) and downstream (Catalyst Monitor) HO2S for proper function.
-
Once the HO2S Monitor is enabled, the upstream HO2S signal voltage
amplitude and response frequency are checked. Excessive voltage is determined
by comparing the HO2S signal voltage to a maximum calibratable threshold
voltage. A fixed frequency closed loop fuel control routine is executed and
the upstream HO2S voltage amplitude and output response frequency are
observed. A sample of the upstream HO2S signal is evaluated to determine if
the sensor is capable of switching or has a slow response rate. A HO2S heater
circuit fault is determined by turning the heater on and off and looking for a
corresponding change in the Output State Monitor (OSM) and by measuring the
current going through the heater circuit. The HO2S Monitor DTCs can be
categorized as follows:
The DTCs associated with HO2S lack of switching are DTCs P1130, P1131,
P1132, P1150, P1151 and P1152.
The DTCs associated with HO2S slow response rate are DTCs P0133 and
P0153.
The DTCs associated with HO2S signal circuit malfunction are DTCs
P0131, P0136, P0151 and P0156.
The DTCs associated with a HO2S heater circuit malfunction are DTCs
P0135, P0141, P0155 and P0161.
The DTC associated with the downstream HO2S not running in on-demand is
DTC P1127.
The DTCs associated with swapped HO2S connectors are DTCs P1128 and
P1129.
-
The MIL is activated after a fault is detected on two consecutive drive
cycles.
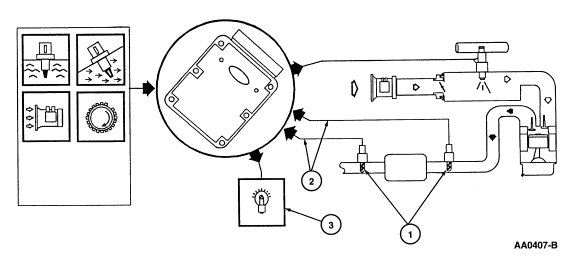
Figure 12: Heated Oxygen Sensor Monitor

