Section 03-07B: Electronic Ignition (EI) System | 1993 Mustang Workshop Manual |
In the EI system, all engine timing and spark distribution is handled electronically with no moving parts. This system has fewer parts that require replacement and provides a more accurately timed spark. During basic operation, the powertrain control module (PCM) 12A650 determines the ignition timing required by the engine and the ignition control module (ICM) 12A297 determines which ignition coil to fire.
EI System Diagram
NOTE: The following diagram is not meant to show detailed wiring interconnections. Refer to vehicle wiring diagrams for this information.
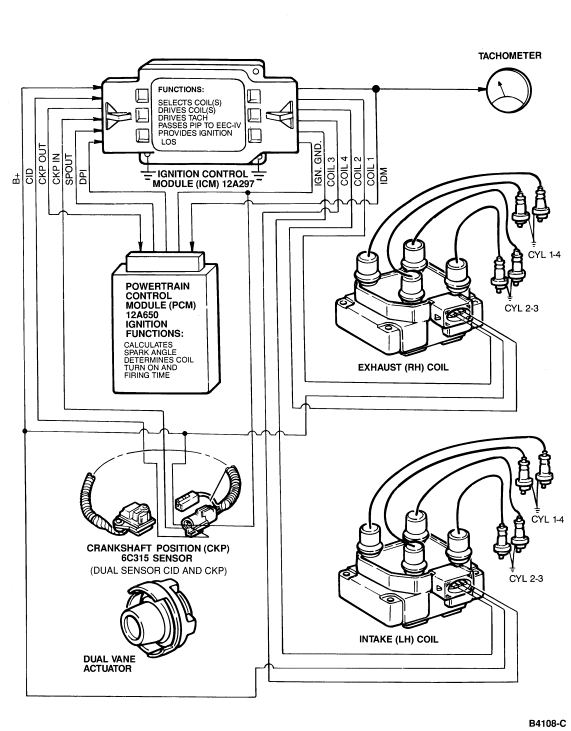
Components
The EI system for the 2.3L dual spark plug engine consists of the following components:
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
The crankshaft position sensor is a dual Hall effect magnetic switch, which is actuated by the dual vane cup on the crankshaft pulley hub assembly. This sensor generates two separate signals, CKP and CID (cylinder identification). The CKP signal provides base timing and RPM information, while the CID signal is used to synchronize the ignition coils. Initial timing (base timing) is set at 10 degrees ± 2 degrees BTDC and is not adjustable.
Ignition Coil Packs
Two ignition coil packs are used for the 2.3L dual plug engine. The two ignition coil packs are triggered by the ICM and are timed by the PCM. Each coil pack contains two separate ignition coils for a total of four ignition coils. Each ignition coil fires two spark plugs simultaneously, one spark plug on the compression stroke and one on the exhaust stroke. The spark plug fired on the exhaust stroke uses very little of the ignition coils stored energy, and the majority of the ignition coils energy is used by the spark plug on the compression stroke. Since these two spark plugs are connected in series, the firing voltage of one spark plug will be negative with respect to ground, while the other will be positive with respect to ground. Refer to the Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Manual for additional information on spark plug polarity.
Ignition Control Module (ICM)
The main function of the ICM is to switch between ignition coils and trigger the coils to spark. The ICM receives the CKP and CID signals from the crankshaft timing sensor, and the SPOUT (spark out) signal from the PCM. During normal operation, CKP is passed on to the PCM and provides base timing and RPM information. The CID signal provides the ICM with the information required to switch between the coils for cylinders 1 and 4 and the coils for cylinders 2 and 3. The SPOUT signal (from the PCM) contains the optimum spark timing and dwell time information. The spark angle is determined by the rising edge of SPOUT, while the falling edge of SPOUT controls the coil current "on" or "dwell" time. The dwell time is controlled or varied by varying the duty cycle (duration) of the SPOUT signal. This feature is called CCD (computer controlled dwell). Therefore, with the proper inputs of CKP, CID and SPOUT the ICM turns the ignition coils on and off in the proper sequence for spark control. CID is also sent to the PCM to allow for Bank to Bank fuel control.
Failure Mode Effects Management
During some EI system faults, the Failure Mode Effects Management (FMEM) portion of the ICM will maintain vehicle operation. If the ICM does not receive the SPOUT input, it will automatically turn the ignition coils on and off using the CKP signal. However, this will result in fixed spark timing (ten degrees BTDC) and a fixed dwell time (no CCD). If the ICM does not receive the CID input during engine cranking, random coil synchronization will be attempted by the module. Therefore, several start attempts (cycling the ignition from OFF to START) may be required to start the engine. If the ICM loses CID input while engine is running, the module will remember the proper firing sequence and continue to fire to maintain engine operation.
Dual Plug Inhibit
Dual Plug Inhibit (DPI) is a function of the PCM that is only used when the vehicle is being started at temperatures -7° C (20° F) and below. During engine cranking, the PCM will only fire the spark plugs on the right hand side of the engine. When the engine has started, the PCM will send a signal to the ICM to start normal dual plug operation.
Ignition Diagnostic Monitor
The Ignition Diagnostic Monitor (IDM) is a function of the ICM. The ICM sends information on system failures to the PCM which stores the information for diagnostic self test. The IDM signal also is used to drive the vehicle instrument tachometer, and test tachometer for system diagnosis.
Additional information on the EI theory of operation is contained in the Powertrain Control/Emissions Diagnosis Manual