 CAUTION: After installing rocker arms, do not rotate crankshaft until tappets
have had sufficient time to bleed down. To do otherwise may cause serious valve
damage. Manually bleeding down will reduce waiting time.
CAUTION: After installing rocker arms, do not rotate crankshaft until tappets
have had sufficient time to bleed down. To do otherwise may cause serious valve
damage. Manually bleeding down will reduce waiting time.
Section 03-00: Engine—Service | 1993 Mustang Workshop Manual |
Tools Required:
Check the lift of each lobe in consecutive order and make a note of the readings.
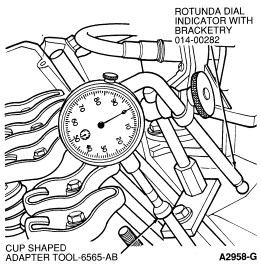
NOTE: If lift on any lobe is below specified service limits, camshaft and tappet operating on worn lobe(s) must be replaced, as well as any tappet showing pitting or having contact face worn flat or concave. Refer to Inspection, Camshaft and Hydraulic Tappets .
 CAUTION: After installing rocker arms, do not rotate crankshaft until tappets
have had sufficient time to bleed down. To do otherwise may cause serious valve
damage. Manually bleeding down will reduce waiting time.
CAUTION: After installing rocker arms, do not rotate crankshaft until tappets
have had sufficient time to bleed down. To do otherwise may cause serious valve
damage. Manually bleeding down will reduce waiting time.
Hydraulic Tappet/Lash Adjuster
Tools Required:
The hydraulic lash adjusters used in the overhead cam 2.3L I-4 engine are zero-lash hydraulic devices similar in construction and operation to the hydraulic tappets used on push rod engines. They are cleaned, inspected and checked in the same manner as hydraulic tappets. The instructions below apply equally to the lash adjuster and the tappet.
Hydraulic tappet noise may be caused by any of the following:
Excessive collapsed tappet gap may be caused by loose rocker arm fulcrum bolts/nuts, incorrect initial adjustment, or wear of tappet face, or worn roller tappets, push rod rocker arm, rocker arm fulcrum or valve tip. With tappet collapsed, check gap between valve tip and rocker to determine if any other valve train parts are damaged, worn or out of adjustment.
A sticking tappet plunger may be caused by dirt, chips, or varnish inside the tappet. The sticking can be corrected by disassembling the tappet and removing the dirt, chips or varnish that are causing the condition.
A tappet check valve that is not functional may be caused by an obstruction such as dirt or chips preventing it from closing when the cam lobe is lifting the tappet, or it may be caused by a broken check valve spring.
Air bubbles in the lubrication system will prevent the tappet from supporting the valve spring load and may be caused by too high or too low an oil level in the oil pan, or by air being drawn into the system through a hole, crack or leaking gasket on the oil pump pickup tube.
If the leakdown time is below the specified time for used tappets, noisy operation may result. If no other cause for noisy tappets can be found, the leakdown rate should be checked and any outside the specification should be replaced.
Assembled tappets can be tested with Hydraulic Tappet Leakdown Tester TOOL-6500-E or equivalent, to check the leakdown rate. The leakdown rate specification is the time in seconds for the plunger to move a specified distance of its travel while under a 22.7 kg (50 lb) load. Test the tappets as follows:
Leakdown Testing
NOTE: Do not mix parts from different tappets. Parts are select-fitted and are not interchangeable.
NOTE: Tappets cannot be checked with engine oil in them. Only testing fluid can be used.
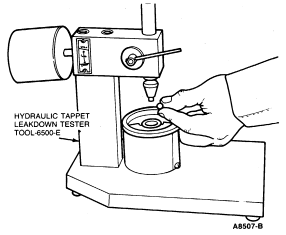
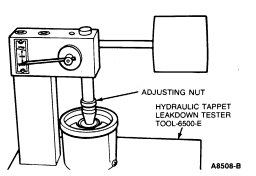
Use center mark on pointer scale as Stop Timing point instead of original Stop Timing mark at top of scale.